What was the origin of the Indus system?
The Indus is one of the longest river systems in Asia. It originated in Mansarovar, Tibet, with an altitude of 5,182 meters and a flow rate of about 2,880 kilometers. The Indus is part of the Himalayan River system, which includes the Ganges and Brahmin Rivers. These Himalayan rivers existed even before the formation of the Himalayan mountains. As for origin, these rivers existed even before the Indian plate collided with the Eurasian plate.
- Observation Skill Test: People with Sharp Eyes try to find the Bugle in 12 Seconds
- Optical Illusion Brain Challenge: If you have Hawk Eyes Find the Number 403 in 15 Secs
- Observation Skill Test: If you have Hawk Eyes find the Word Snack among Smack in 20 Secs
- Optical Illusion: Can you find 661 among 681 in 8 Seconds? Explanation and Solution to the Optical Illusion
- Optical Illusion Eye Test: Identify the Clown Toy in this Picture within 15 Seconds If You Have Sharp Vision

Source: indiawris.gov.in
In this article, we will explore the Indus River, its tributaries and its civilization in detail.
Also read: What is the Indus Water Treaty? Check the history and significance of this agreement
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rxrb_9bgdti
Also read: Pakistan’s history occupying Kashmir (POK)
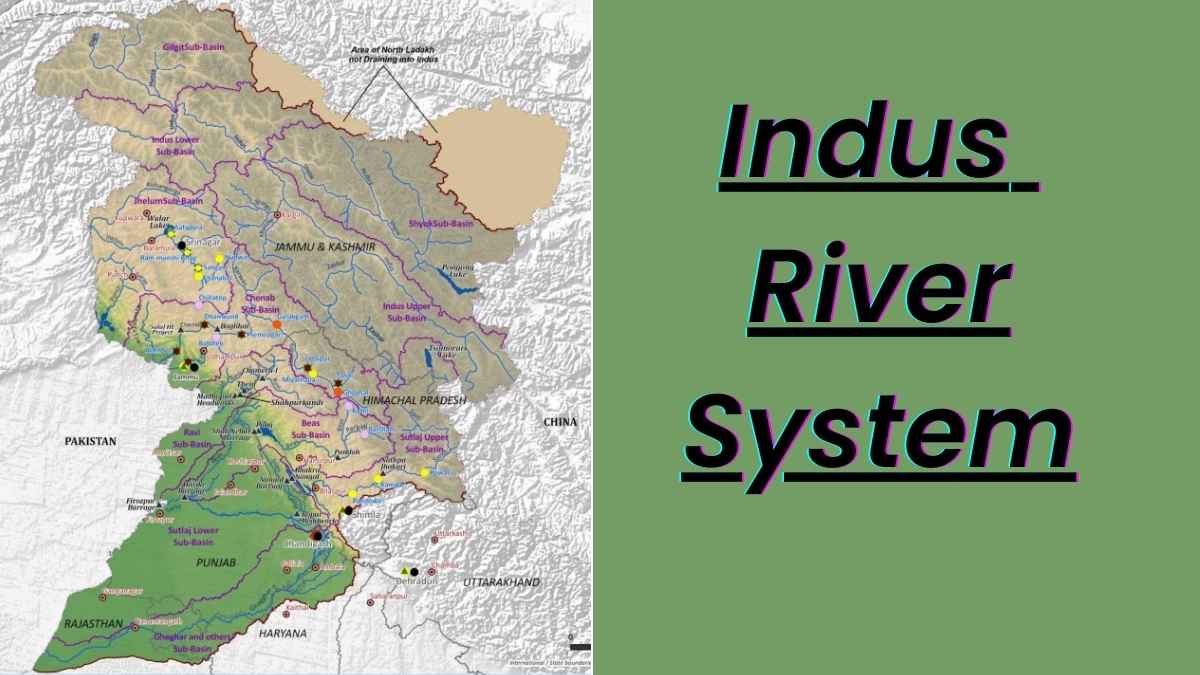
Indus River Drainage System
|
Different names of the Indus River |
The well-known language of the Indus |
|
Faith |
Sanskrit |
|
Sinthos |
Greek |
|
Sindtus |
Latin |
The Indus River Basin extends from Tibet (China) and India to Afghanistan and Pakistan, covering an area of about 11,65,500 square kilometers. In India, it covers almost Jammu and Kashmir, Himaal Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan, Haryana and Chandigarh. It is almost 2880 km, and in India, its length is nearly 1,114 km. The Indus River basin is surrounded by the Himalayas in the east, the karakoram mountains in the north and the Haramosh range from the north, Sulaiman and Kirthar range from the west, and to the south, it is covered by the Arabian Sea.
It flows northwest from Mansarovar Lake until it reaches the Nanga Parbat Mountains.
Indus Civilization
The Indus system played a very important role in the development of ancient civilizations, including the Indus civilization. As we know, the Indus civilization is the oldest civilization in the world and the earliest urban culture in the northwest region of the Indian subcontinent. It is one of the oldest civilizations among the Mesopotamians and Egyptians. Its history can be traced back to 3300 BC to 1300 BC. Many locations were found in this civilization, such as the Harapa civilization and Moonjo Daro.
What are the salient characteristics of the Indus system?
|
Significant characteristics of Indian watershed (until the border) |
|
|
Basin range longitude latitude |
72°28′ to 79°39’e 29°8′ to 36°59’n |
|
Length of the Indus River (km) |
See more : Why are Olive Ridley Turtles crucial for ocean health? 1114 (in India) |
|
Water catchment area (SQ.KM.) |
321289 |
|
Average Water Resources Potential (MCM) |
73310 |
|
Available surface water resources (MCM) |
46000 |
|
Real-time storage capacity (MCM) for completed projects |
16222.0 |
|
Real-time storage capacity (MCM) for projects under construction |
100.00 |
|
Total real-time storage capacity of the project (MCM) |
16322.00 |
|
CWC’s Hydrological Observatory |
26 |
|
CWC’s Flood Prediction Station |
0 |
Physics of the Indus System
The Indus River Basin is covered by an area of 11,65,500 square kilometers, which is located in Tibet, India, Afghanistan and Pakistan. On the table, how many states does the Indus flow through and flow through its drainage areas:
|
state |
Drainage area (square kilometer) |
|
Jamuk and Kashmir |
193,762 |
|
Himaal Pradesh |
51,356 |
|
Punjab |
50,304 |
|
Rajasthan |
15,814 |
|
Haryana |
9,939 |
|
Chandigarh |
114 |
|
All |
321,289 |
Tributary of the Indus River System
The Indus River system includes 5 rivers in total, namely Jhelum River, Chenab River, Ravi River, Beas River and Satluj River.
1. Jhelum River:

Source: indiawris.gov.in
Jhelum originated in Verinag, southeast of the Kashmir Valley. It flows from north to Wular Lake; from here, it changes the route southward and then flows into the hills of the Balamula Mountains. From here it requires a steep narrow path through the PIR Panjal range. The Jhelum River established a zigzag curve in Muzaffarabad, where a 170-km border between India and Pakistan was established before appearing with the Potwar Plateau.
2. Chenab River:

Source: indiawris.gov.in
The Chenab River originates from the Bara Lacha Pass of Lahul Spiti, part of the Zanskar series. After the merger of the two rivers, Chandra and Bhaga will establish the chenab river in Tandi. The Chenab River is also known as Chandrabhaga. On this river alone, the world’s tallest railway bridge was built.
3. Ravi River:

Source: indiawris.gov.in
The Ravi River originates from Kullu Hills in Rohtang Pass, Himaal Pradesh. The Ravi River is usually discharged in areas within the Pir Panjal and Dhaola. After crossing the Chamba district and reaching the Punjab plains, it took the southwest and moved to Pakistan below Amritsar.
4. Bis River:

Source: indiawris.gov.in
The Beas River originates from Rohtang Pass at the southern end of the Pir Panjal Mountains, which is close to the source of the Ravi River. It travels southwest along the Dhaola Dhar Mountains, and from there, in the Harike Lake in Punjab, it meets the Satluj River before flowing into Pakistan.
5. Staluj River

Source: indiawris.gov.in
The Satluj River, also sometimes called the Red River, originates from the southern slope of the Kailash Mountain near Mansarovar Lake and Rakas Lake. Before entering Shipki La, it travels through different regions of Himaal: Kinnaur, Shimla, Kullu, Kullu, Solan, Mandi and Bilaspur. In Himachal, after Shipli La, it entered the Punjab Plains near Bhakra, where only the world’s highest gravity dam, the Bhakra Nangal Dam, was built on this river.
in conclusion
Therefore, it is all about the Indus River system, which plays an important role in India’s economy and agriculture. Since it has five tributaries, the branches are Jhelum River, Chenab River, Ravi River, Beas River and Staluj River, mainly through northern India, many hydroelectric dams were built to enable India to generate electricity.
Source: https://dinhtienhoang.edu.vn
Category: Optical Illusion